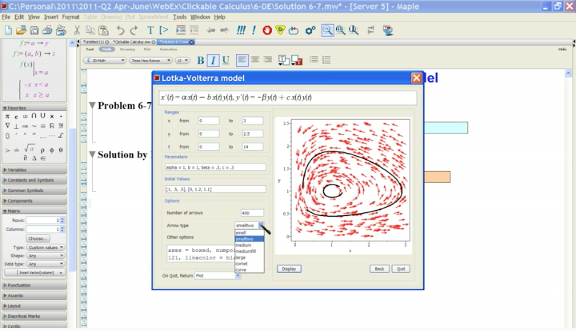
The Lotka–Volterra equations, also known as the predator–prey equations, are a pair of first-order, nonlinear, differential equations frequently used to describe the dynamics of biological systems in which two species interact, one as a predator and the other as prey. The populations change through time according to the pair of equations:
where
 and
and  represent the growth rates of the two populations over time;
represent the growth rates of the two populations over time;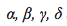 are positive real parameters describing the interaction of the two species.
are positive real parameters describing the interaction of the two species.The Lotka–Volterra system of equations is an example of a Kolmogorov model, which is a more general framework that can model the dynamics of ecological systems with predator–prey interactions, competition, disease, and mutualism.1
Maple is powerful math software that makes it easy to learn about Lotka-Volterra equations, and to analyze, explore, visualize, and solve mathematical problems from virtually every branch of mathematics. Student pricing available.
1 Source: Wikipedia